As a potent antioxidant carotenoid, astaxanthin may support eye health, assist with inflammation management, aid exercise recovery, and provide overall cellular protection against oxidative stress.
Astaxanthin is a type of carotenoid known as a xanthophyll, which is a pigment that gives plants a red-pink color. It also gives many animals their color, including birds and some shellfish. Dr. Basil Weedon headed the group that first synthesized astaxanthin in 1975. The human body doesn’t convert astaxantin into vitamin A, unlike some other carotenoids and carotenes. It is therefore safe and effective, with no known toxic effects.
Common dietary sources of astaxanthin include shellfish, such as crayfish, krill, shrimp and other crustaceans. Fish such as salmon and trout also contain significant amounts of this pigment. Additional dietary sources of astaxanthin include a variety of algae and yeast. The most significant commercial source is Haematococcus pluvialis, a species of microalgae that contains 40,000 parts per million of astaxanthin. Yeast in the Phaffia genus and Artic shrimp are also commercially significant sources of astaxanthin.
Astaxanthin is commonly used as a food coloring for animals, especially fish. It is also a popular dietary supplement for people. The same molecular structure that gives astaxanthin its color provides it with a strong antioxidant property, meaning that it may help support the body’s ability to manage damage caused by free radicals. This property makes astaxanthin beneficial for a variety of health conditions.
The use of astaxanthin as an antioxidant is its primary value as a dietary supplement. It is especially helpful for maintaining vision, managing healthy inflammation and recovering from exercise.
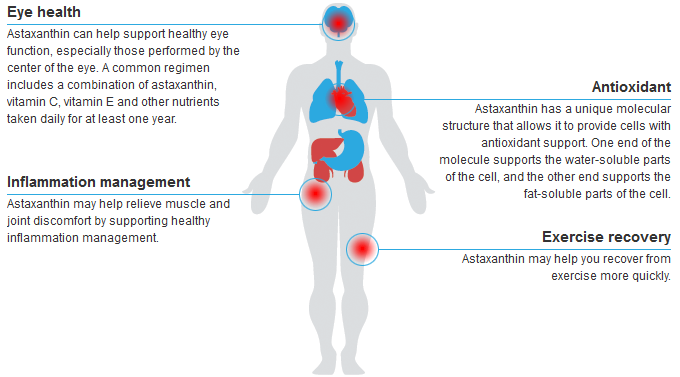
Astaxanthin can help support healthy eye function, especially those performed by the center of the eye. A common regimen includes a combination of astaxanthin, vitamin C, vitamin E and other nutrients taken daily for at least one year.
Astaxanthin may help relieve muscle and joint discomfort by supporting healthy inflammation management.
Astaxanthin has a unique molecular structure that allows it to provide cells with antioxidant support. One end of the molecule supports the water-soluble parts of the cell, and the other end supports the fat-soluble parts of the cell.
Astaxanthin may help you recover from exercise more quickly.
You may benefit from astaxanthin if you suffer from the many effects of excess free radicals. These include mental aging effects such as poor recall and physical effects like the deterioration of motor skills, and joint discomfort. Astaxanthin, may also help support healthy digestion.
Shipping calculated at checkout
